Discoid Lupus Erythematosus (DLE)
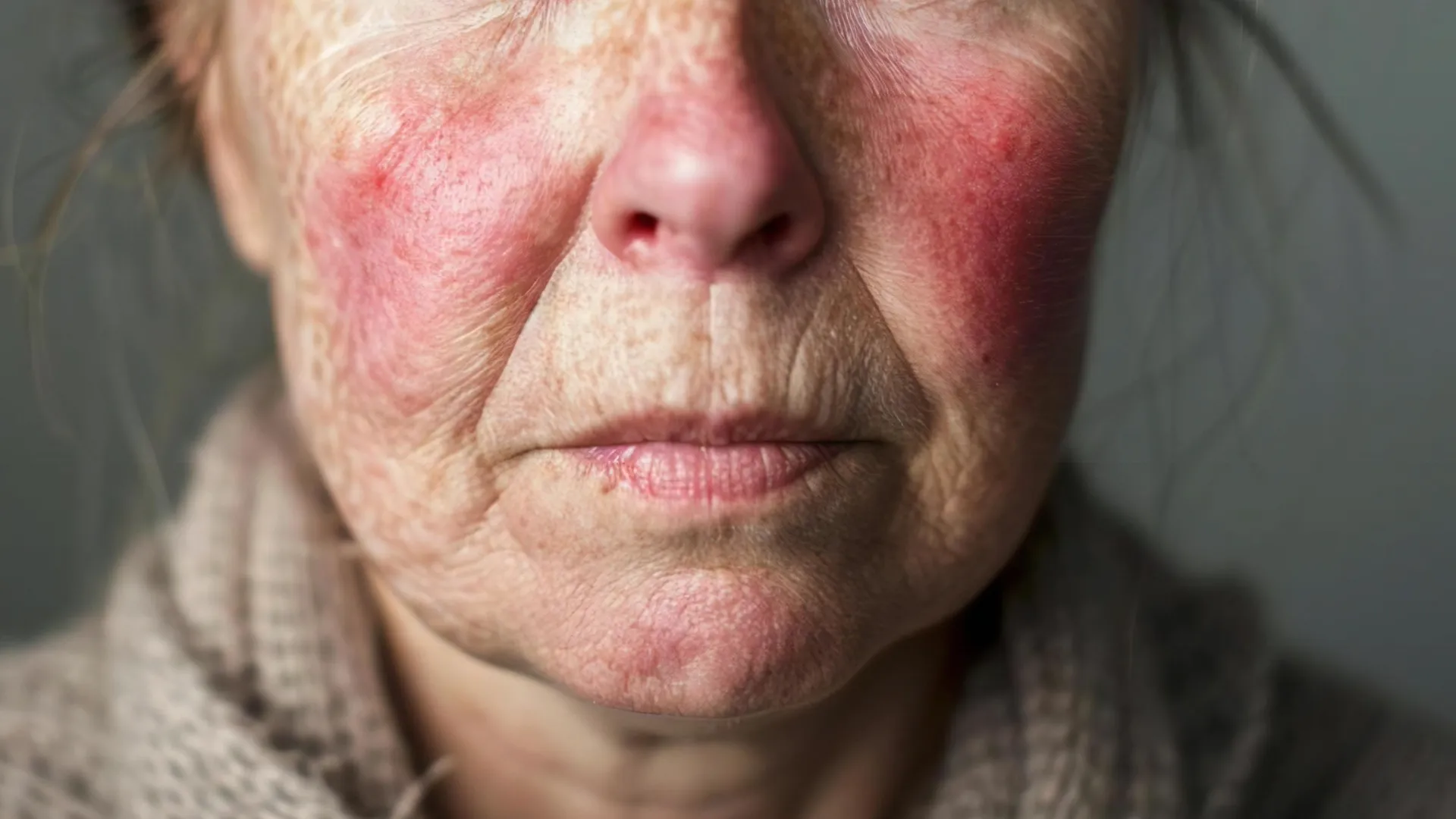
Discoid Lupus Erythematosus (DLE) is a chronic skin condition that is a form of lupus erythematosus, primarily affecting the skin. It is characterized by round, disc-shaped lesions that can appear anywhere on the body but are most commonly found on the face, scalp and ears (sun exposed areas). While DLE is not life-threatening, it can lead to scarring and changes in skin pigmentation.
Symptoms
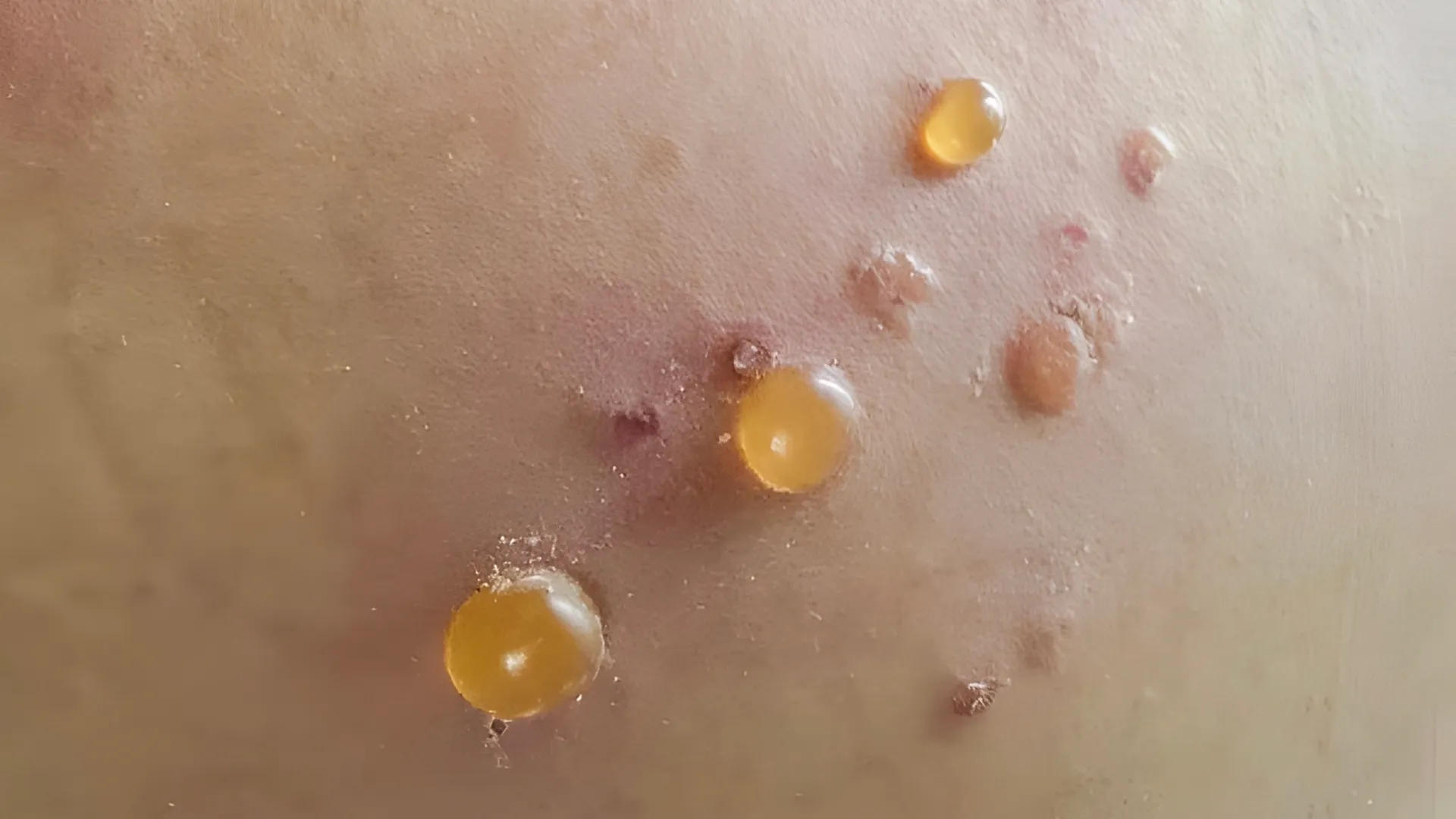
The hallmark of DLE is the appearance of coin-shaped, red, scaly patches. These lesions may:
- Itch or burn
- Form crusts or scabs
- Leave scars upon healing
- Result in hair loss if lesions occur on the scalp
Causes
The exact cause of DLE remains unclear, but it is believed to involve a combination of genetic, environmental and immunological factors. Sun exposure can exacerbate symptoms, making UV protection crucial for affected individuals.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis is typically made through a clinical examination by a dermatologist, often confirmed with a skin biopsy. Blood tests may also be performed to rule out systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) or other conditions.
Treatment
Treatment focuses on managing symptoms and preventing flare-ups. Options include:
- Topical corticosteroids: To reduce inflammation and itching.
- Calcineurin inhibitors: Such as tacrolimus or pimecrolimus, for sensitive areas.
- Antimalarials: Medications like hydroxychloroquine may be prescribed for more extensive lesions.
- Sun protection: Wearing sunscreen and protective clothing is essential to prevent exacerbation.