Mycosis
Fungal infections of the skin and its appendages include mycosis of the skin, scalp and nails. They are classified as superficial or deep, depending on the depth of involvement.
Categories of Mycosis
Fungal infections are categorized based on the fungus causing the infection into:
- Dermatophytes: Responsible for the majority of fungal infections. They are divided into three main genera: Microsporum, Trichophyton and Epidermophyton.
- Candidiasis: Caused by the yeast Candida albicans or other species.
- Pityrosporum infections: Caused by the yeast Pityrosporum orbiculare.
- Onychomycosis: Infections affecting the nails.
- Rare mycoses
Clinical Forms of Dermatophytosis
- Scalp dermatophytosis: Located on the scalp, affecting the skin, hair and hair follicles. It is more common in children and the elderly. Symptoms vary from mild scaling to severe inflammation.
- Beard dermatophytosis: Affects the skin and hair in the beard area, presenting with circular red lesions.
- Tinea faciei (Facial dermatophytosis): Found on the face, torso and limbs, characterized by red plaques that expand peripherally with central healing.
- Tinea cruris (Groin dermatophytosis): Affects the groin folds with red plaques and intense itching, especially in summer due to sweating.
- Tinea pedis (Athlete’s foot): The most common site of dermatophytosis, causing scaling and fissures in the spaces between the toes.
- Tinea Manuum (Hand dermatophytosis): May be asymptomatic and progress slowly.
Candidiasis
Candidiasis is a superficial fungal infection that affects the skin, mucous membranes and nails, caused by the yeast Candida.
Predisposing factors
- Age
- Pregnancy
- Excessive moisture
- Immunological disorders
- Hormonal disorders
- Obesity
- Antibiotic use
Clinical picture
- Oral candidiasis: White plaques on the tongue and oral cavity.
- Genitalia:
- Women: Whitish or yellowish vaginal discharge with intense itching.
- Men: Red papules and vesicles on the glans.
- Both genders may have erosions and fissures.
- Skin folds: Red, moist surfaces, often accompanied by itching.
- Nails: Local redness and swelling around the nails.
Pityriasis versicolor
Pityriasis versicolor is caused by the lipophilic yeast Pityrosporum orbiculare (or Malassezia furfur). It appears as multiple circular white, brown or pink spots with scaling, primarily on the upper torso, but it can extend to the arms, neck and abdomen.
Causes of Development:
- Increased temperature and humidity.
- Hyperactivity of sebaceous glands (more common in teenagers and young adults).
- Immune system disorders.
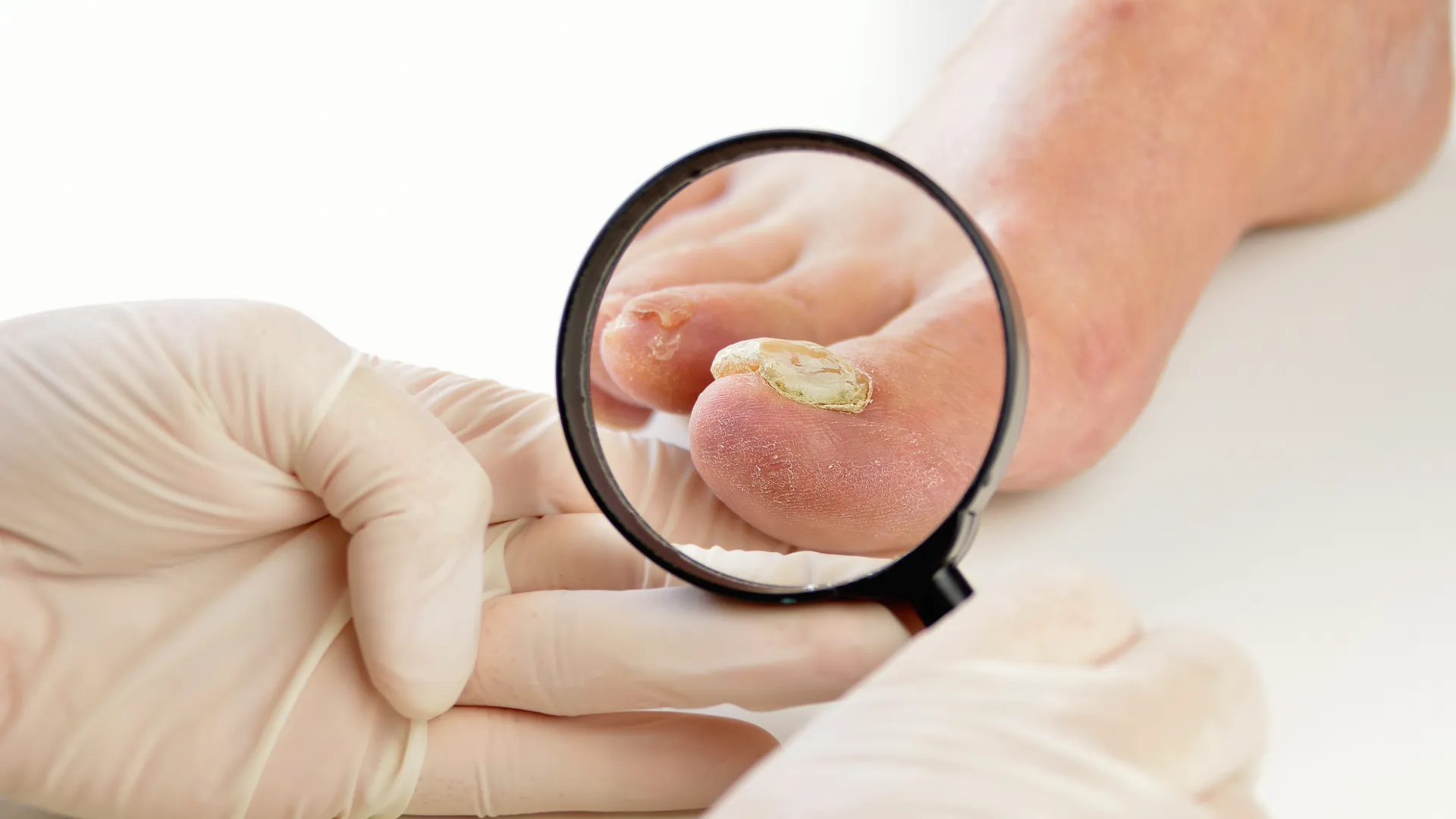
Onychomycosis
Onychomycosis is a fungal infection that affects the nails. It is usually caused by dermatophytes but can also be due to Candida. It often manifests with thickening, discoloration, and separation of the nail. An unpleasant odor may accompany it. The disease does not resolve without specific treatment. It is more common in the elderly and diabetics.
Diagnosis of mycosis
- Clinical examination
- Medical history
- Sampling for microscopic examination and culture
- Biopsy
Treatment
The treatment depends on the type of mycosis, the location and extent of involvement, and the patient’s underlying conditions.
- Topical Treatment: Topical antifungal preparations for mild cases.
- Systemic Treatment: Oral antifungal medications are mainly given for extensive infections, infections of the scalp or beard, and when there is no response to topical treatments.
- Antifungal shampoos
- Laser therapy
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What are the most common causes of fungal infections?
Common causes include excessive moisture, poor hygiene, and immunological disorders. - How can I prevent fungal infections?
Keep your skin and nails clean and dry, avoid wet shoes, and use antifungal products. - How long does treatment last?
The duration of treatment depends on the type and severity of the infection, usually ranging from a few weeks to several months. - Are fungal infections contagious?
Some fungal infections, like athlete’s foot, can be contagious through direct or indirect contact (e.g., shared footwear). - What should I do if the treatment is ineffective?
Consult your doctor for a possible adjustment of the treatment.
Conclusion
Fungal infections are common and can affect the quality of life. It is important to recognize and treat them promptly.