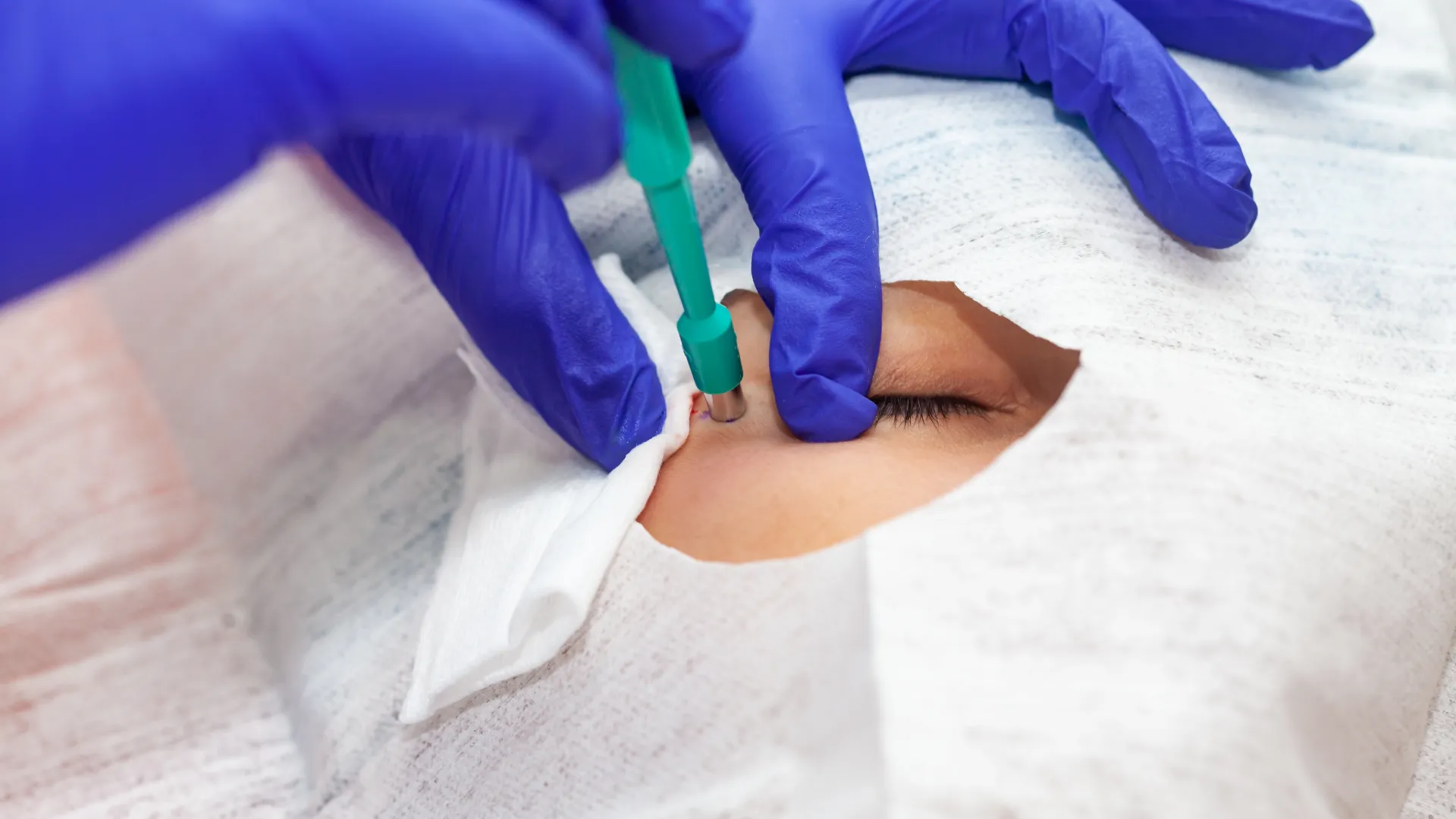
Skin biopsy
A skin biopsy is one of the most important clinical procedures in dermatology. It is used for various reasons, including:
- Differential diagnosis: When a skin rash may indicate multiple different conditions.
- Diagnosis confirmation:
- Malignancy Assessment: To determine the presence and stage of a skin tumor.
The process of skin biopsy involves collaboration between the dermatologist and the pathologist.
Types of biopsy
- Shave biopsy: Primarily suitable for superficial lesions (elevated or exophytic).
- Punch biopsy: A special tool is used to remove a cylindrical piece of skin. The size and depth of the biopsy may vary.
- Excisional biopsy: The complete surgical removal of a lesion, followed by closure of the wound.
Biopsy procedure
Before the biopsy, the dermatologist will take a detailed medical history, including information about chronic conditions, use of anticoagulant medications and allergies.
After that, local anesthesia is administered at the biopsy site. The procedure includes:
- Removal of the skin sample.
- Closure of the wound.
Stitches are typically removed after a few days, depending on the area of the body. During the healing process, the use of antiseptic and antibiotic cream is recommended. After stitch removal, a reparative cream is suggested.
The sample is sent for histological examination, and in some cases, specialized tests such as immunofluorescence or immunohistochemistry may be required.
Complications
Skin biopsy is generally safe and quick, with minimal complications. The most common include:
- Bacterial infection.
- Stitch breaking.
- Poor wound healing.
These complications are usually avoided by following the postoperative instructions.