Urticaria
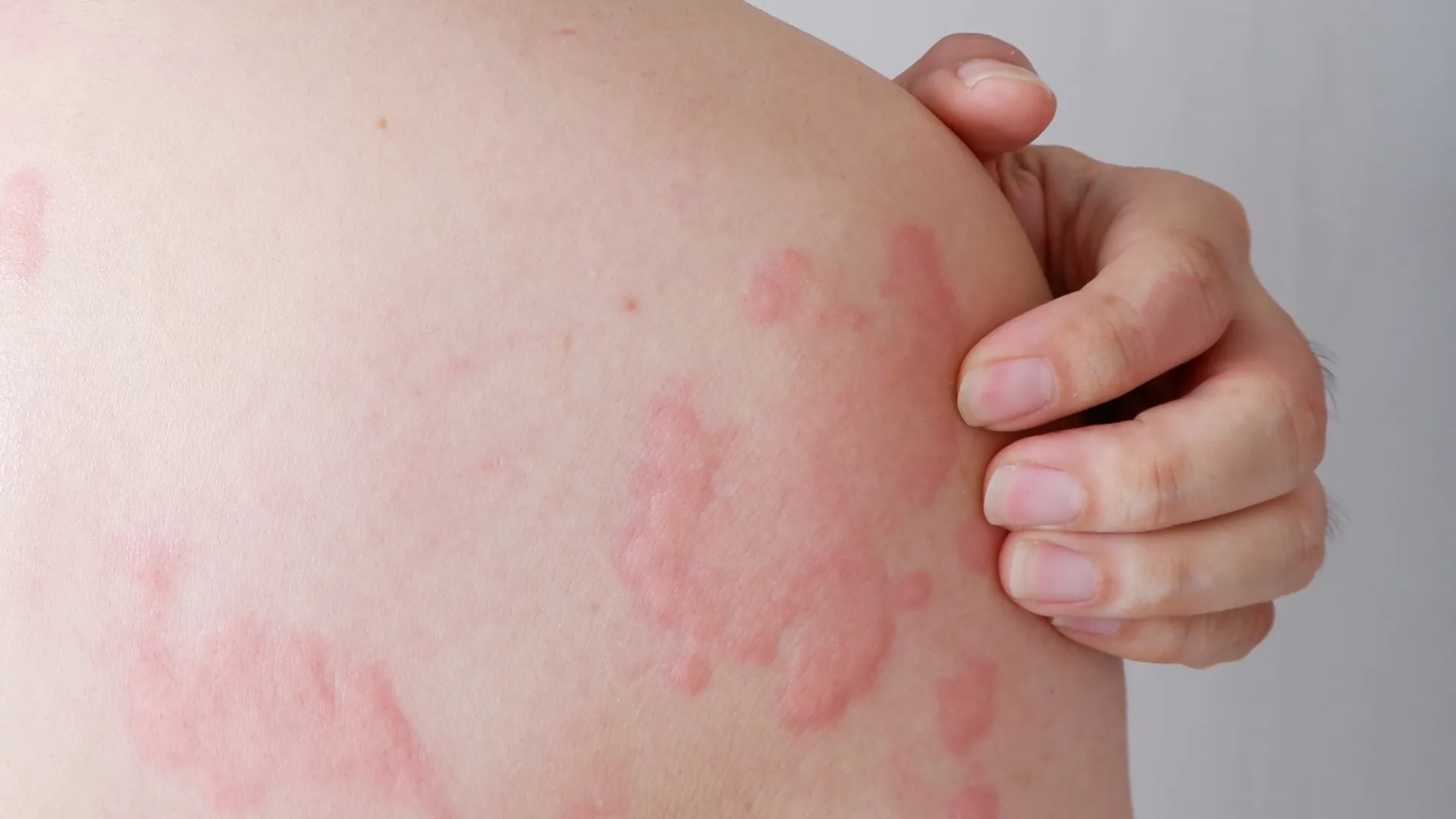
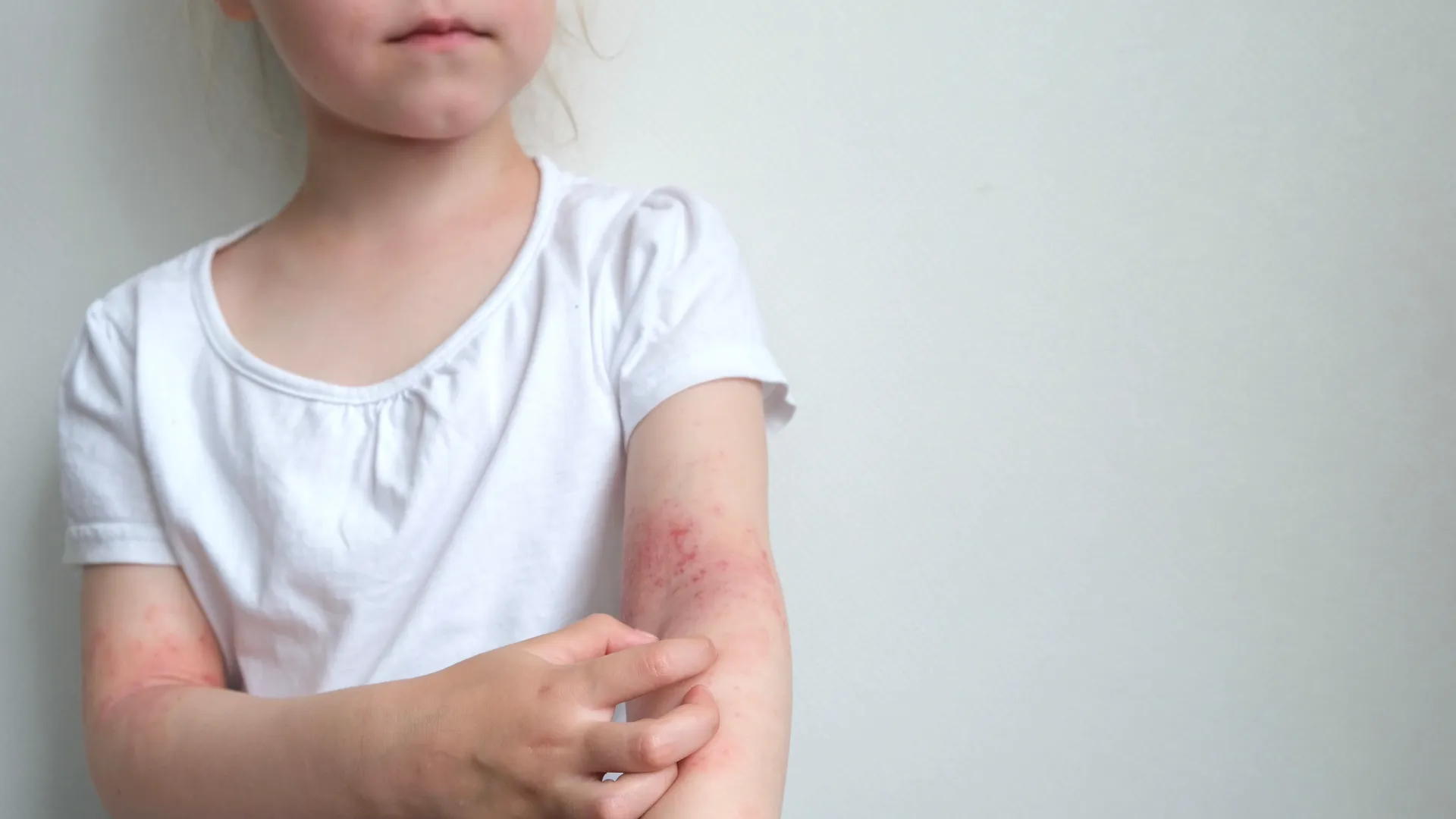
Urticaria is a skin rash that appears in the form of red, swollen patches (hives) on the skin. The lesions appear suddenly and can be either transient or persistent, causing intense itching or a burning sensation.
Urticaria can occur in various areas of the body, affecting daily activities and the general well-being of the person. Sometimes, the lesions may merge, creating larger areas with plaques. The duration of symptoms can vary from a few hours to months or even years, with periods of flare-ups and remissions.
Causes
Urticaria can have many and varied causes. Some of the most common include:
- Foods: Nuts, eggs, shellfish, and other allergenic foods.
- Medications: Antibiotics (penicillin, sulfonamides), anti-inflammatory drugs (ibuprofen).
- Insect bites.
- Physical stimuli: Such as cold, heat, pressure, physical activity or exposure to the sun.
- Infections: Bacterial (e.g., urinary tract infections, pharyngitis) and viral (common cold, infectious mononucleosis, etc.).
- Pets: Can cause allergic reactions in some individuals.
- Pollen and plants: Certain plants such as oak and ivy.
- Urticaria can also occur without an obvious cause.
Symptoms
The symptoms of urticaria can last from a few minutes to months or even years. Some of the characteristic symptoms include:
- Rash (hives): Red or pale plaques with clear edges, which usually appear suddenly and subside quickly.
- Shape change: The plaques may move, grow or shrink within a short period.
- Itching or burning sensation: The affected area may cause discomfort and itching is almost always present.
- Duration: Each individual plaque lasts no more than 24 hours, while the rash may reappear repeatedly.
Patients often experience angioedema in addition to the characteristic urticarial rash. Angioedema is swelling (edema) beneath the skin, and this swelling usually lasts 24-48 hours.
It is important to recognize the symptoms and seek medical attention, especially if there is swelling of the throat or difficulty breathing (angioedema), which could be life-threatening.
Forms of urticaria
Acute Urticaria
The duration of the rash is up to 6 weeks.
Chronic Urticaria
Chronic urticaria lasts more than six weeks and occurs almost daily. In this case, the lesions may cause continuous itching, but each rash lasts less than 24 hours and does not leave scars or pigmentation.
The causes of chronic urticaria may include:
- Disorders of the immune system.
- Hormonal imbalances or thyroid problems.
- In rare cases, cancer or other serious conditions.
If there is no clear cause for the urticaria, the condition is termed chronic idiopathic urticaria.
Treatment
The treatment of urticaria depends on the severity and duration of the symptoms. In mild cases, antihistamines are the first line of defense. These medications relieve itching and reduce inflammation.
For chronic urticaria, treatment options include:
- Combination of antihistamines.
- Corticosteroids: Used only for short-term relief of symptoms.
- Antibiotics: When urticaria is related to infections.
Monoclonal antibody (Omalizumab): In cases that do not respond to other treatments, Omalizumab, an anti-IgE agent, can be used to block the immune system reactions that cause urticaria.
Prevention
- Avoid known allergens and irritants, such as foods, medications or insecticides that may cause a reaction.
- Use moisturizing creams and products to soothe the skin.
- Wear comfortable clothing and avoid heat or humidity, which may exacerbate symptoms.