Seborrheic Dermatitis
Seborrheic dermatitis is a common and chronic skin condition that causes redness, flaking and oily crusts on the skin. Although it is not dangerous, it can cause discomfort and concern due to its appearance. It often affects areas of the skin where sebaceous glands are most active, such as the face, scalp, chest and ears. Seborrheic dermatitis can occur in individuals of all ages and the symptoms may vary depending on the patient’s age.
Causes and risk factors
The exact cause of seborrheic dermatitis is not fully understood, but it is believed to be related to the excessive proliferation of a microorganism called Malassezia, which normally resides on the skin. Factors that can worsen the condition include:
- Hormonal changes: During puberty, pregnancy or menopause.
- Stress: Can exacerbate symptoms.
- Cold and dry climates: Symptoms worsen in the winter.
- Weak immune system: Such as in patients with HIV.
- Genetic predisposition.
Symptoms
The symptoms of seborrheic dermatitis include:
- Red patches of skin, often covered with oily, yellowish or white scales.
- Itching in the affected areas.
- Flaking of the skin
- On the scalp, it may appear as dandruff or more severe skin peeling.
Clinical presentation
The clinical presentation varies depending on the age group.
Infants
In infants, seborrheic dermatitis appears as the well-known cradle cap, primarily on the scalp. It consists of oily, yellowish crusts that may spread to the forehead, eyebrows or even behind the ears. While the condition may seem concerning, it typically resolves with the use of mild shampoos or ointments.
Children and teenagers
In children and teenagers, seborrheic dermatitis can affect the scalp, leading to dandruff and itching. Its appearance may be linked to hormonal changes during puberty. Additionally, the use of cosmetics or hair products can worsen the condition.
Adults
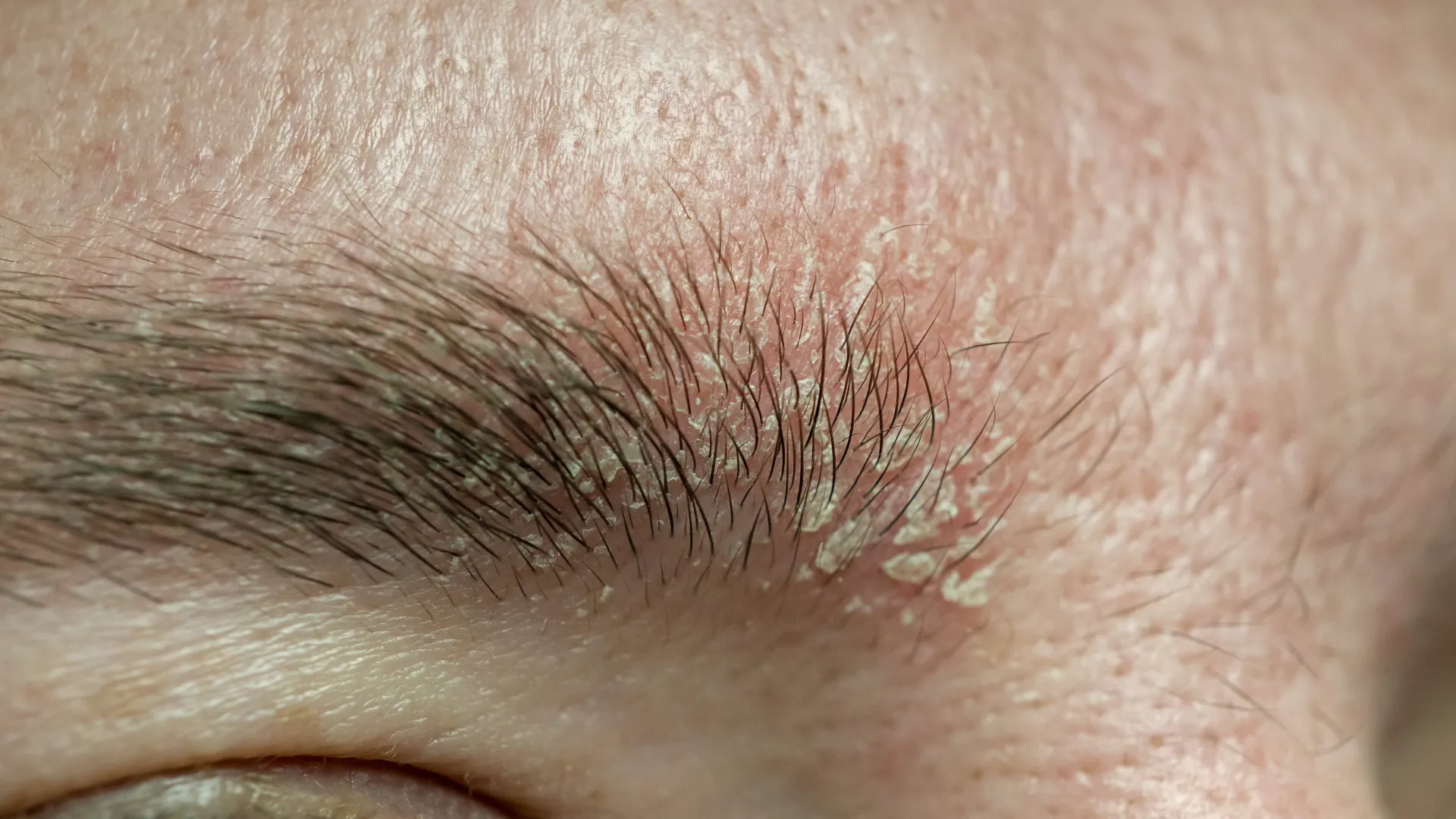
In adults, seborrheic dermatitis is more commonly found on the face, particularly around the nose, eyebrows, upper lip, as well as on the chest and behind the ears. Stress, weather changes and poor diet can exacerbate symptoms.
When located in the skin folds, it appears as a bright red rash, often accompanied by cracks.
In some cases, the condition may be associated with other skin disorders, such as rosacea or psoriasis.
Treatment
Treatment of seborrheic dermatitis depends on the severity and the patient’s age. The main treatment options include:
- Antifungal soaps and shampoos: Soaps containing ingredients like ketoconazole are often helpful in treating the condition.
- Topical treatment: The application of topical treatments in the form of lotions or creams (topical corticosteroids, calcineurin inhibitors) is usually sufficient to soothe the rash.
- Systemic treatment: In more severe cases, oral antifungal treatment may be prescribed.
Prevention
- Cleanliness and moisturization: Daily washing with mild soaps and moisturizing with products suitable for the skin type can help manage the condition.
- Stress management: Reducing stress can help minimize flare-ups.
- Avoiding irritating products during flare-ups.
- Avoiding scratching the scales: To prevent the risk of secondary infection.
Conclusion
Seborrheic dermatitis is a chronic, but manageable condition that affects individuals of all ages. Although it is not dangerous, early diagnosis and treatment are important for relieving symptoms and preventing flare-ups.