Melanoma
Melanoma is a type of skin cancer that develops in melanocytes, the cells responsible for producing melanin – the pigment that gives our skin its color. Although it is less common than other forms of skin cancer, it is more dangerous as it can metastasize to other parts of the body.
Risk Factors
The primary cause of melanoma is excessive exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation, either from the sun or artificial sources, such as tanning beds.
Other risk factors are:
- People with fair skin, red hair, and blue eyes (skin types prone to burning).
- A history of severe sunburns, particularly in childhood.
- Individuals with a large number of moles, especially dysplastic ones.
- A family history of melanoma.
- A weakened immune system.
Symptoms
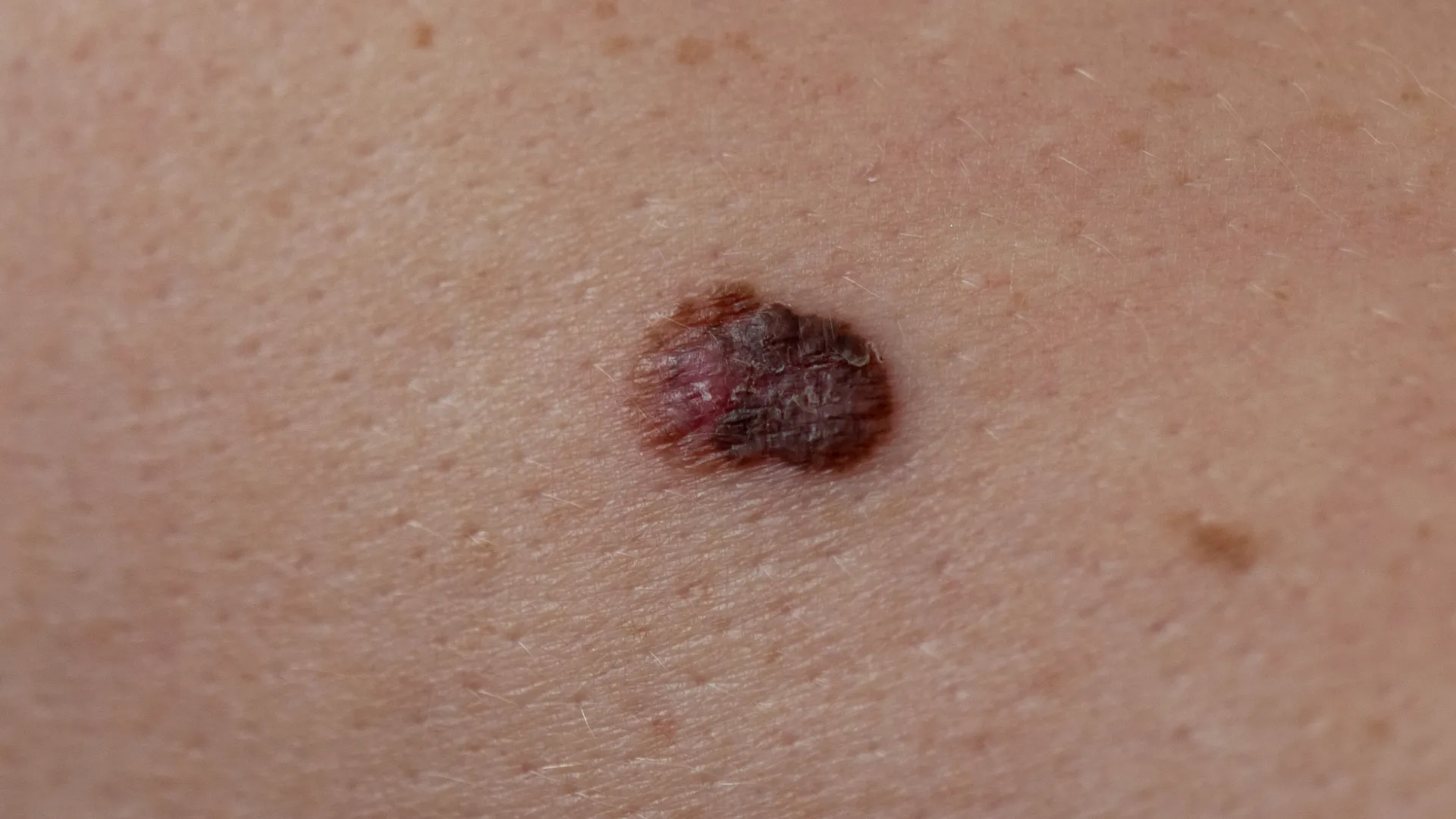
Melanoma often appears as a change in an existing mole or as a new lesion on the skin. Early detection relies on the ABCDE method:
- A (Asymmetry): Asymmetry in the shape of the mole.
- B (Border): Irregular or unclear borders.
- C (Color): Changes in color, such as multiple shades.
- D (Diameter): Diameter larger than 6 millimeters.
- E (Evolution): Any changes in size, shape,or color.
Types of Melanoma
Melanoma can present in various forms depending on its growth pattern and location.
Superficial spreading melanoma
The most common type, which accounts for about 70% of cases. It usually starts as a flat or slightly raised lesion with irregular borders and a mix of colors, including brown, black, red and blue. This type is predominantly seen in individuals with fair skin and in areas exposed to the sun.
Nodular melanoma
This type is more aggressive and represents approximately 15-20% of cases. It typically appears as a dome-shaped nodule that can be black, blue, red or sometimes colorless (amelanotic). This type grows rapidly and penetrates deeper into the skin.
Acral lentiginous melanoma
This is a rarer type, often found on the palms, soles or under the nails (subungual melanoma). It is more commonly seen in individuals with darker skin tones but can affect anyone.
Lentigo maligna
Mainly occurs in older adults in areas of chronic sun exposure, such as the face and hands. It begins as a slowly spreading pigmented lesion and remains on the surface for some time before penetrating deeper layers.
Amelanotic melanoma
This is a rare type of melanoma that lacks pigment. It appears as pink, red or skin-colored lesions, making it more difficult to diagnose.
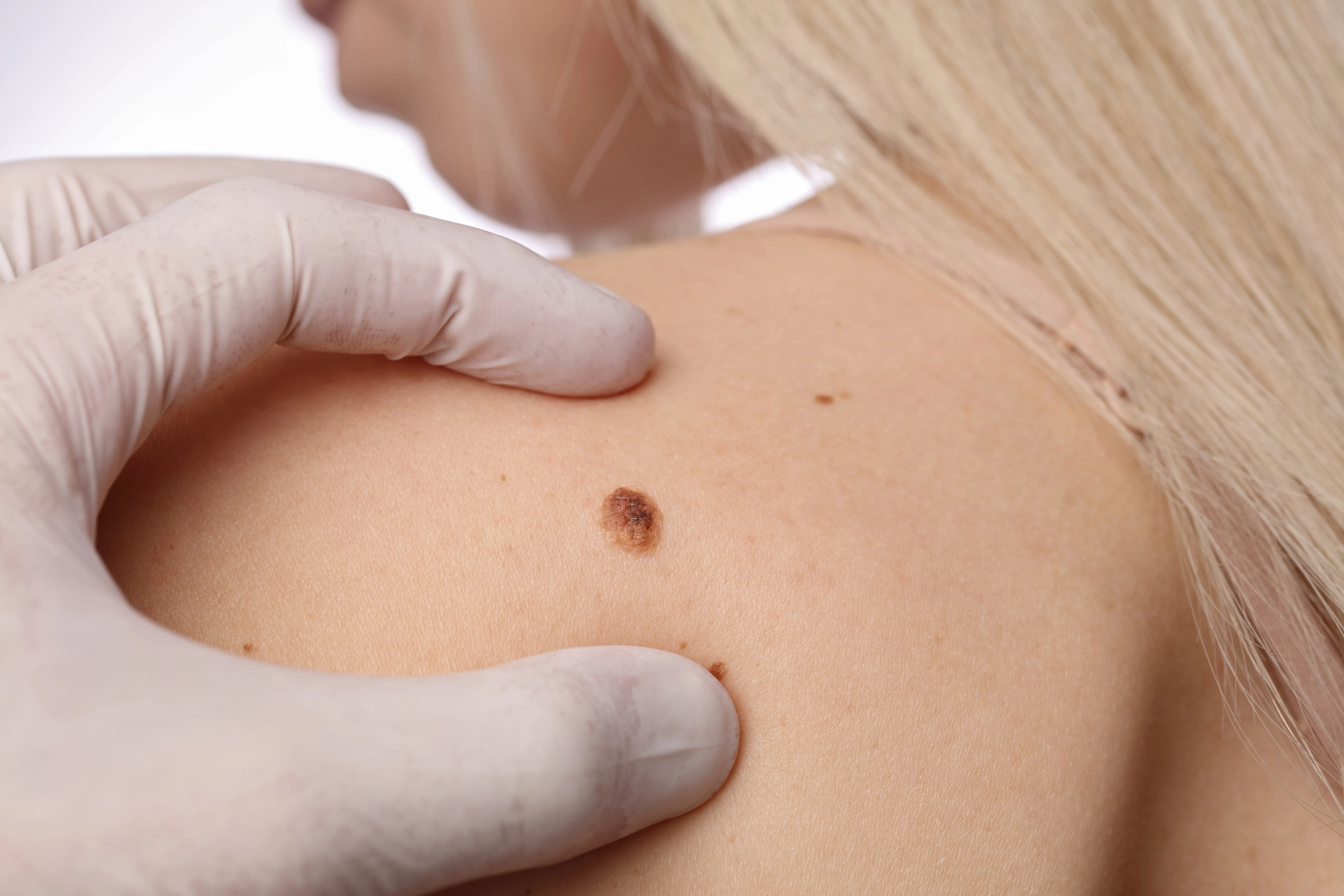
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of melanoma is based on clinical examination and dermatoscopic evaluation of moles. It is confirmed through a biopsy, which provides a definitive diagnosis and determines the stage of the cancer.
Treatment
Treatment depends on the stage of melanoma. A biopsy determines the tumor stage and potential metastases. Based on this staging, a personalized treatment plan is developed in collaboration with an oncologist.
Prevention
Since melanoma is an aggressive tumor that develops quickly and can metastasize, early detection is crucial. The entire population, especially high-risk groups, should undergo annual dermatoscopic examinations. In some cases, mole mapping may also be necessary.
Additional preventive measures include:
- Sunscreen use: Daily application with SPF 30 or higher.
- Sun protection: Wearing hats, sunglasses and UV-protective clothing.
- Avoid tanning beds.
- Regular self-examinations: Check your skin monthly, and if you notice any concerning changes, contact our clinic immediately.