Warts
Overview
Warts are benign skin lesions caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV). They can affect individuals of all ages, but are most commonly seen in children and adolescents, especially during the summer months. Warts spread through direct contact between individuals or indirectly through contaminated surfaces, such as swimming pools and locker rooms. The virus typically enters the skin through small cuts, abrasions, or cracks. Although they are not dangerous, warts can cause pain and difficulties in daily life (especially those on the soles of the feet). Because they are particularly contagious, they should be treated promptly.
Types of Warts
Warts are divided into three main categories:
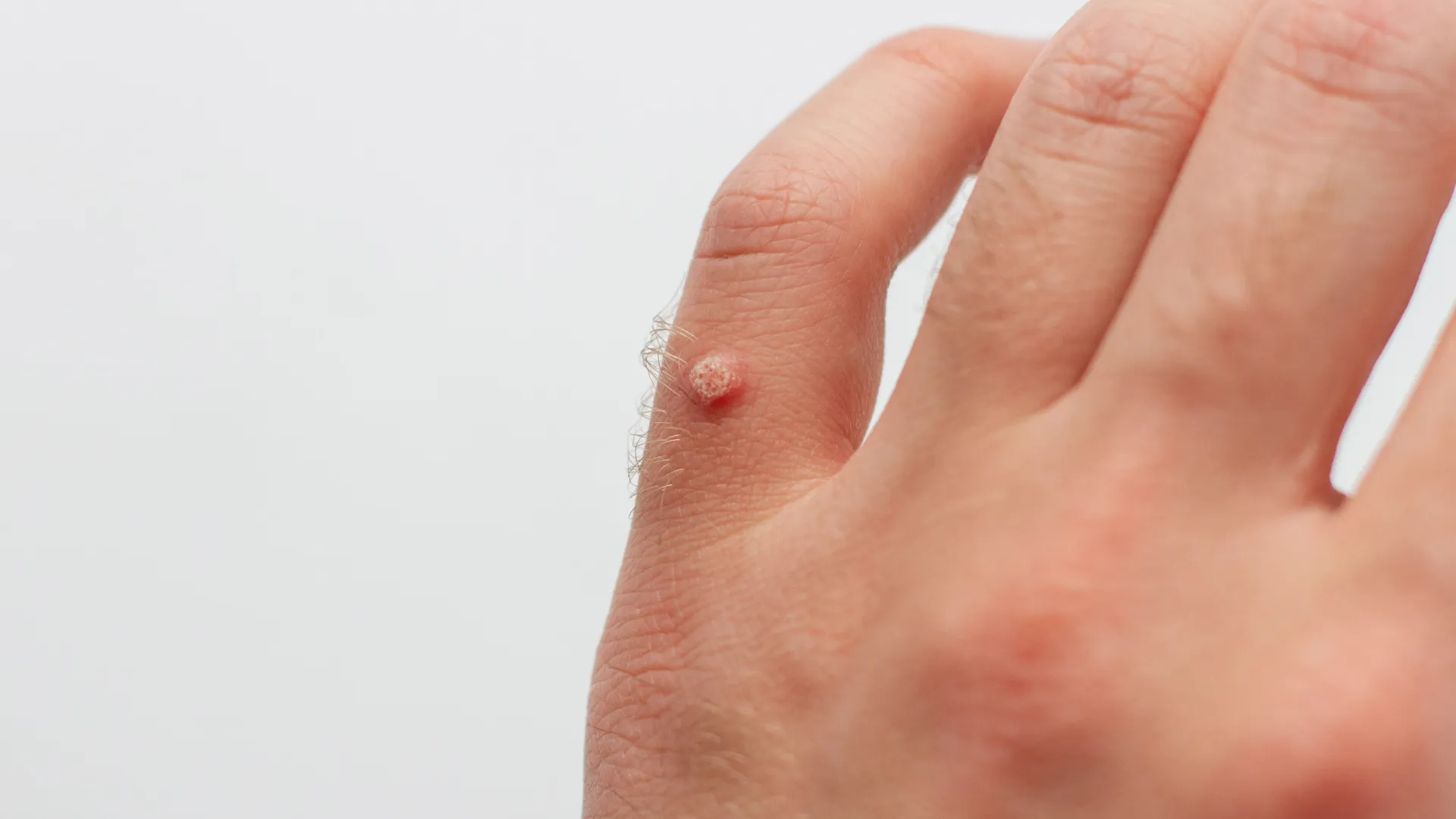
Common Warts (Verruca vulgaris)
Small, rounded bumps (papules) that are the color of the skin. They mainly appear on the hands and fingers, as well as on the elbows, knees, or face.
Plantar Warts (Verruca plantaris)
Located on the soles of the feet. They can cause pain while walking as they often grow inward.
Flat Warts (Verruca plana)
Flat bumps with a smooth surface, which may be reddish or the color of the skin. Usually found on the face, shins, and hands.
Treatment
While many warts resolve on their own as the immune system fights off the virus, treatment is often recommended to prevent transmission. Common methods for removing warts include:
Cryotherapy
Freezing the wart with liquid nitrogen. The extreme cold destroys the cells of the wart, allowing for natural healing. Local anesthesia is not required. The procedure is quick and painless and patients can return to their regular activities immediately. Multiple sessions may be needed for complete removal.
Electrosurgery
Electric current is applied to the wart, generating heat that eliminates the wart cells. A local anesthetic is used prior to the procedure.
CO2 Laser
This approach uses a focused beam of light to target and destroy wart tissue. A local anesthetic is applied prior to the procedure.
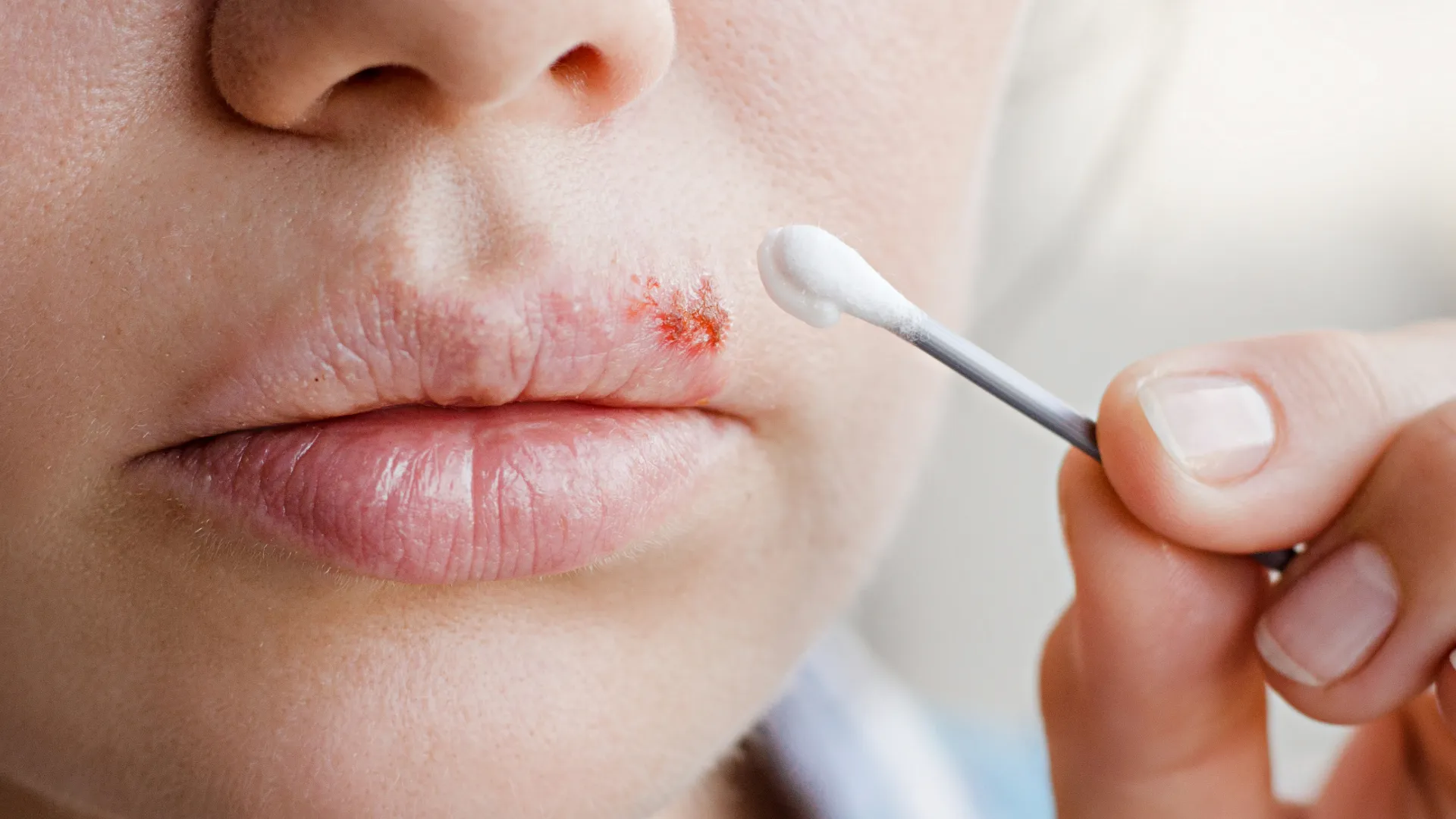
Topical Solutions
Treatments such as monochloroacetic acid and salycilic acid can be applied directly to the wart.
Common Questions
How can I prevent infection from warts?
- Use good hygiene measures, such as regular handwashing and keeping feet dry
- Avoid sharing personal items, like towels or footwear, to reduce the risk of transmission
- Use flip-flops in public places like pools and locker rooms
What should I watch out for if I have warts?
Avoid touching them, and wash your hands afterward. If you have plantar warts, change your socks more frequently. Avoid shaving in the area and friction with towels. Do not share shoes, socks, or towels.
Do warts go away on their own?
They may eventually resolve on their own over a long period, but there is a risk of significant spreading during this period.
Who is prone to developing warts?
Warts can be transmitted at any age, but they are more frequently seen in children, individuals with weakened immune systems and patients with atopic dermatitis.